Disclaimer: This information is provided as-is for the benefit of the Community. Please contact Sophos Professional Services if you require assistance with your specific environment.
Table of Contents
- Overview
- Prerequisites
- Step 1: Create Azure Local Network Gateway (with Sophos Firewall public IP details)
- Step 2: Create a Gateway Subnet
- Step 3: Create the VPN Gateway
- Step 4: Create the VPN connection (Azure)
- Step 5: Download and extract the needed information from the configuration file (Azure)
- Step 6: Create the VPN connection (Sophos Firewall)
- Step 7: Create firewall rules to allow inbound and outbound traffic through the VPN (Sophos Firewall)
- Step 8: Configure the xfrm tunnel interface (Sophos Firewall)
- Step 9: Configure static routing to the Azure VNET Gateway (Sophos Firewall)
- Step 10: Configure BGP routing to the Azure network (Sophos Firewall)
- Step 11: Enable Dynamic Routing
- Step 12: Verify the VPN connection
- Things to watch out for
Overview
This recommended read describes how to configure Azure VPN gateway IP sec connection with BGP.
Prerequisites
1. Sophos Firewall 18 firmware
- A minimum of "EAP 3 Refresh-1" is needed
- See Sophos Firewall and UTM: Firmware and installer download links
2. Your On-Prem Sophos Firewall and the following information:
- The public IP of Sophos Firewall.
- The IP address space behind your Sophos Firewall
3. Your Microsoft Azure vNet and the following information:
- IP address space of the vNet
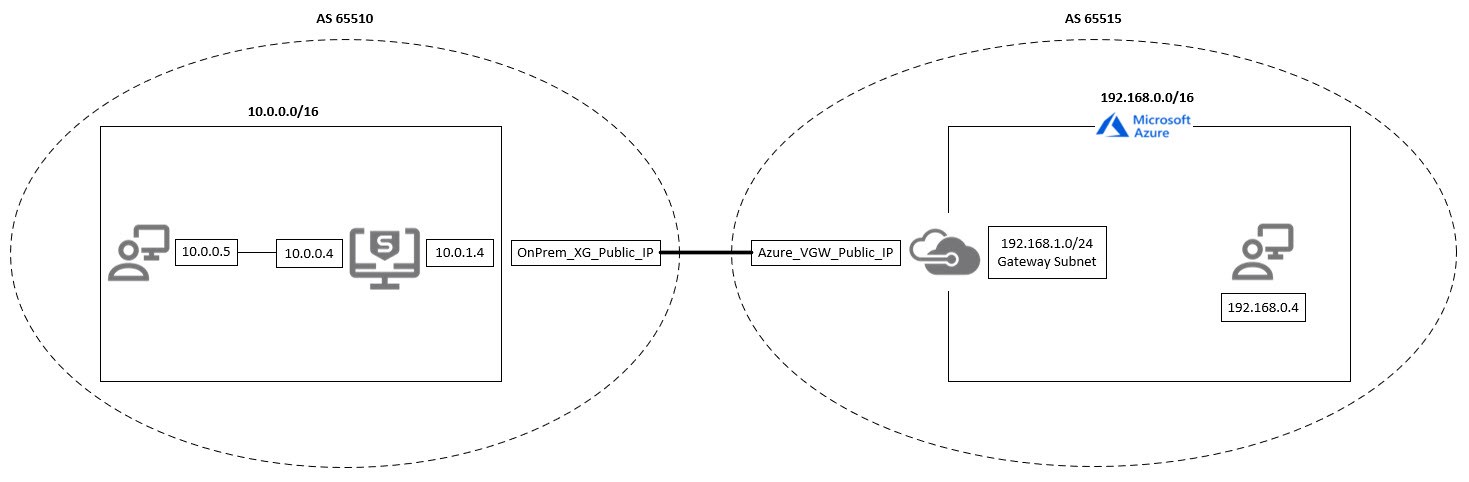
Step 1: Create Azure Local Network Gateway (with Sophos Firewall public IP details)
The local network gateway typically refers to your on-premises location. You will need the public IP address of your On-Prem Sophos Firewall and your On-Prem Private IP address spaces.
Please note that this configuration assumes that the public IP address is directly configured on the On-Prem Sophos Firewall. Your configuration will be slightly different if your On-Prem Sophos Firewall sits behind a NAT device.
- Go to the Azure Portal: https://portal.azure.com and sign in with your credentials.
- Click Create a resource.
- In the search box, type Local network gateway.
- Select Local Network Gateway and click Create.
-
In the Create local network gateway blade, configure the following and then click Create:
- Subscription: Verify that the correct subscription is selected for the deployment.
- Resource group: Select the resource group that you want to use. You can either create a new resource group or select an existing one.
- Region: Select the location that this object will be created in.
- Name: On_Premises_Sophos_XG_Firewall (You can give this any preferred name).
- Endpoint: IP address
- IP address: Specify the public IP address of your Sophos Firewall.
- Address space: Specify the address ranges for the network that your On-Prem local network represents. In our scenario, this is 10.0.0.0/16.
-
Click Next: Advanced. Configure the following.
- Configure BGP settings: Yes
- Autonomous system number (ASN): The ASN of your Sophos Firewall. In this scenario, it is 65510.
Note: A BGP-enabled connection between two network gateways requires their ASNs to differ. Additionally, the following ASNs are reserved by Azure: 8075, 8076, 12076 (public), 65515, 65517, 65518, 65519, 65520 (private). When connecting to Azure VPN gateways, you can't specify these ASNs for your on-premises VPN devices. While setting up IPsec connectivity from virtual network gateways to Azure virtual WAN VPN, the ASN for Local Network Gateway must be 65515. - BGP peer IP address: WAN IP of your Sophos Firewall. In this scenario, it is 10.0.1.4.
- Click Next: Review + Create.
- Click Create.
Step 2: Create a Gateway Subnet
The VPN gateway will be deployed into a specific subnet of your network called the 'GatewaySubnet'. The size of the GatewaySubnet that you specify depends on the VPN gateway configuration that you want to create. While it is possible to create a GatewaySubnet as small as /29, it is recommend to create a larger subnet that includes more addresses by selecting /27 or /28 to be able to accommodate future configurations.
- In the Azure Portal: https://portal.azure.com, click More services.
- In the search box, type Virtual Networks and select the Virtual Networks option.
- Click the virtual network for which you want to create a virtual network gateway.
- In the Virtual Networks blade, under Settings, click Subnets.
- Click + Gateway subnet to add a new Gateway subnet in the Subnets blade.
- In the Add subnet blade, configure the CIDR range of the new Gateway subnet and click Save. In this scenario, this is 192.168.1.0/24.
Step 3: Create the VPN Gateway
- In the Azure Portal: https://portal.azure.com, click Create a resource.
- In the search box, type Virtual network gateway.
- Select Virtual Network Gateway and click Create.
-
In the Create virtual network gateway blade, configure the following:
- Subscription: Verify that the correct subscription is selected for the deployment.
- Instance details
- Name: This will be the name of the gateway object you’re creating.
- Region: Select the same location as your virtual network (Otherwise, the virtual network won’t be displayed on the list).
- Gateway type: VPN
- VPN type: Route-based (this is a MUST to use IKEv2).
- SKU: Select the gateway SKU from the drop-down. For more information about gateway SKUs, see Gateway SKUs.
- Generation: Generation 1
- Virtual network: Choose the virtual network to which you want to add this gateway (if the virtual network you want isn’t displayed on the list, verify that you have selected the right location in the Region parameter above).
- Public IP address:
- Public IP address: Create new
- Public IP address name: Enter a public IP address resource name.
- Configure BGP: Enabled
- Autonomous system number (ASN): 65515
Note: Azure virtual network gateways are assigned a default ASN of 65515. Note that a BGP-enabled connection between two network gateways requires that their ASNs be different. You can change the ASN now or after the gateway has been created if needed. - Leave other settings as default.
- Click Review + Create.
- Click Create.
- Creating a gateway can take up to 45 minutes!
- After the VPN gateway creation has been completed successfully, obtain its public IP address (this will be needed in step 6).
- In the Azure Portal, click More services and search for Virtual network gateways. Then click Virtual Network Gateways.
- Click the VPN Gateway that you just created.
- In the Virtual network gateway blade, in the Overview section, note the gateway's public IP address.
- This will be used in step 6.
Step 4: Create the VPN connection (Azure)
- In the Azure Portal: https://portal.azure.com, click More Services and search for Virtual network gateways. Then click Virtual Network Gateways.
- Select the VPN gateway that you created earlier.
- In the Virtual network gateway blade, in the Settings section, click Connections, then click + Add.
- In the Add connection blade, configure the following:
- Name: Sophos_Xg_OnPrem_To_Azure (Input your preferred name)
- Connection type: Site-to-site (IPSec)
- Virtual network gateway: The value is fixed because you are connecting from this gateway.
- Local network gateway:
- Click Choose a local network gateway.
- In the Choose a local network gateway blade, select the local network gateway that you created earlier.
- Shared key (PSK): Input a complex shared key. The value here must match the value we will use on our on-premises Sophos Firewall.
- Enable BGP: Enabled
- IKE Protocol: IKEv2
- The remaining values for Subscription, Resource Group, and Location are fixed.
- Click OK to create your connection. You’ll see the Creating connection flash on the screen.
Step 5: Download and extract the needed information from the configuration file (Azure)
- Click More services in the Azure Portal: https://portal.azure.com and search for Virtual network gateways. Then click Virtual Network Gateways.
- Select the VPN gateway that you created earlier.
- In the VPN Gateway blade, click Connections in the Settings section, then select the connection you created earlier.
- Click the Download Configuration button. This configuration file contains the information needed to configure the Sophos Firewall's VPN connection.
- In the Download configuration blade, select the following:
- Device vendor: Generic Samples
- Device family: Device Parameters
- Firmware version: 1.0
- Click Download Configuration.
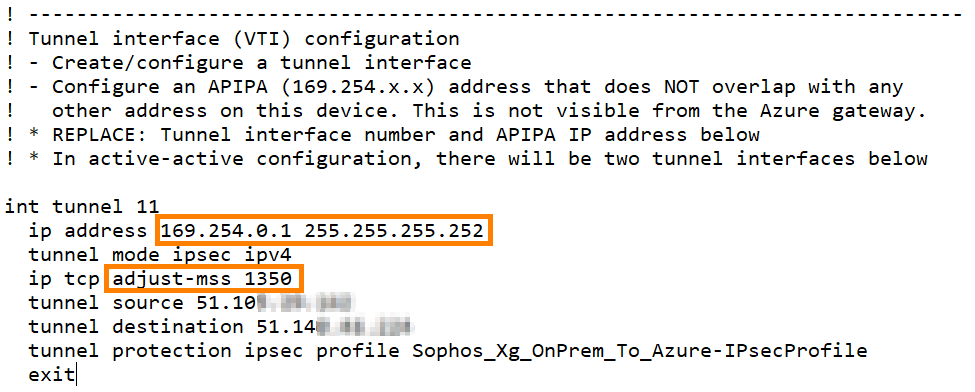
- Open the downloaded file and make a note of the following:
- Scroll down to the Tunnel Interface (VTI) configuration section.
- Make a note of the interface tunnel IP address and subnet mask
- Also, make a note of the MSS value.
- Both values will be needed to configure the xfrm tunnel interface on the Sophos Firewall.
Step 6: Create the VPN connection (Sophos Firewall)
- Sign in to the WebAdmin of your On-Premises Sophos Firewall.
- Under Configure, click VPN → IPSEC connections → Add.
- Configure the following settings:
- General settings
- Name: Input any preferred name.
- Connection type: Tunnel interface
- IP version: Dual
- Gateway type: Respond Only
- Activate on save: Selected
- Description: Add a description of the connection.
- Encryption
- Policy: Microsoft Azure
- Authentication type: Preshared key
- Preshared key: Enter the same preshared key you entered when creating the VPN connection on Azure.
- Repeat preshared key: Confirm the preshared key.
- Gateway settings
- Listening interface: Select the WAN interface of Sophos Firewall.
- Gateway address: Input the public IP of the Azure VPN gateway that you noted in Step 3 (5).
- Local ID type: IP Address
- Remote ID type: IP Address
- Local ID: Enter the public IP of the On-Prem Sophos Firewall.
- Remote ID: Input the public IP of the Azure VPN gateway that you noted in Step 3 (5).
- There’s no option to configure the Local subnet and Remote subnet. It’ll both be set to 0.0.0.0/0.
- Advanced
- Leave default settings.
- Click Save.
- Click OK when prompted about the Preshared key.
- The connection should now be active. Click the red button under Connection to enable the connection.
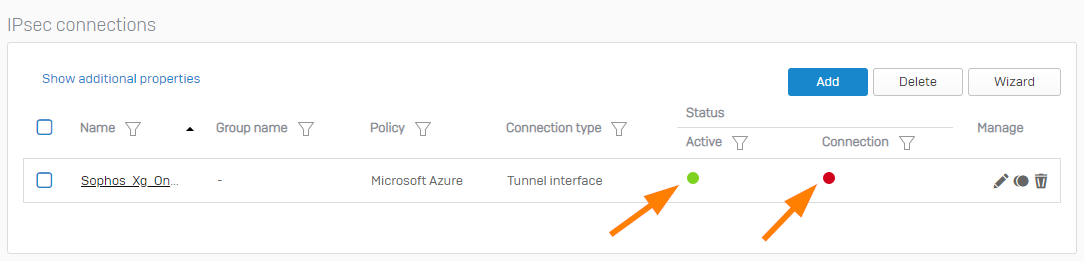
- When prompted, if you’re sure that you want to connect, click OK.
- General settings
Step 7: Create firewall rules to allow inbound and outbound traffic through the VPN (Sophos Firewall)
- Sign in to the WebAdmin of your On-Premises Sophos Firewall.
- Under Protect, click Rules and policies → Add firewall rule → New firewall rule.
- In the Add firewall rule window, configure the incoming firewall rule as follows:
- Rule status: None
- Rule name: azure_to_onprem
- Action: Accept
- Rule position: Top
- Rule group: None
- Log firewall traffic: Selected
- Source
- Source zones: LAN and VPN
- Source networks and devices: Any
- During scheduled time: Leave the default setting
- Destination & services
- Destination zones: LAN and VPN
- Destination networks: Any
- Services: Any
- Leave other settings as default.
- You can configure the security checks of Sophos Firewall for the traffic if required.
- Click Save.
Step 8: Configure the xfrm tunnel interface (Sophos Firewall)
- Sign in to the WebAdmin of your On-Premises Sophos Firewall.
- Under Configure, click Network → Interfaces. Click the WAN interface so that the xfrm interface will be displayed, then click the xfrm interface.
- Under General settings, configure the following:
- IPv4/netmask: Enter the IP address and select the subnet mask you noted in Step 5 (6).
- Expand Advanced settings.
- Select Override MSS and enter the MSS value that you noted in Step 5 (6).
- Click Save.
- In the Update interface prompt, click Update interface.
Step 9: Configure static routing to the Azure VNET Gateway (Sophos Firewall)
- Sign in to the WebAdmin of your On-Premises Sophos Firewall.
- Under Configure, click Routing → Static routing.
- Under IPv4 unicast route, click Add and configure the following:
- Destination IP / Netmask: The Azure Virtual network gateway's Default Azure BGP peer IP address. You can use a subnet mask of /32. In this scenario, it’s 192.168.1.254/32.
Note: To see the Default Azure BGP peer IP address, go to Virtual network gateway, select your VPN gateway, and click Configuration. - Gateway: You can leave this empty or enter the second IP address in the network you noted in Step 5 (6). For example, the Sophos Firewall's tunnel interface in this scenario is 169.254.0.1 in a /30 network, so the only other IP in that network is 169.254.0.2. This can be entered optionally.
- Interface: Select the Sophos Firewall's xfrm tunnel interface.
- Distance: Leave default setting.
- Destination IP / Netmask: The Azure Virtual network gateway's Default Azure BGP peer IP address. You can use a subnet mask of /32. In this scenario, it’s 192.168.1.254/32.
- Click Save.
Step 10: Configure BGP routing to the Azure network (Sophos Firewall)
- Sign in to the WebAdmin of your On-Premises Sophos Firewall.
- Under Configure, click Routing → BGP.
- Under Global configuration, configure the following:
- Router ID: The WAN IP address of your Sophos Firewall. In this scenario, it’s 10.0.1.4.
- Local AS: The ASN of your Sophos Firewall. In this scenario, it’s 65510.
- Click Apply.
- Under Neighbors, click Add and configure the following:
- IPv4 address: The Default Azure BGP peer IP address of the Azure Virtual network gateway. In this scenario, it’s 192.168.1.254.
Note: To see the Default Azure BGP peer IP address, go to Virtual network gateway, select your VPN gateway, and click Configuration. - Remote AS: The ASN of the Azure Virtual network gateway. In this scenario, it’s 65515.
- IPv4 address: The Default Azure BGP peer IP address of the Azure Virtual network gateway. In this scenario, it’s 192.168.1.254.
- Click Save.
- Under Networks, click Add and configure the following:
- IPv4/netmask: The LAN network and subnet mask of your Sophos Firewall. In this scenario, it’s 10.0.0.0/16.
- Click Save.
Step 11: Enable Dynamic Routing
- Go to Administration > Device access and enable Dynamic Routing for the VPN zone.
- Click Apply.
Step 12: Verify the VPN connection
- Do a connectivity test from an on-premise instance to an Azure VM.
- Do a connectivity test from an Azure VM to an on-premise instance.
- In the Azure Portal: https://portal.azure.com, go to Virtual network gateways and select the virtual network that you connected to.
- In the Virtual network gateway blade, in the Settings section, click Connections.
- In the Virtual network gateway | Connections blade, ensure the connection status is Connected.
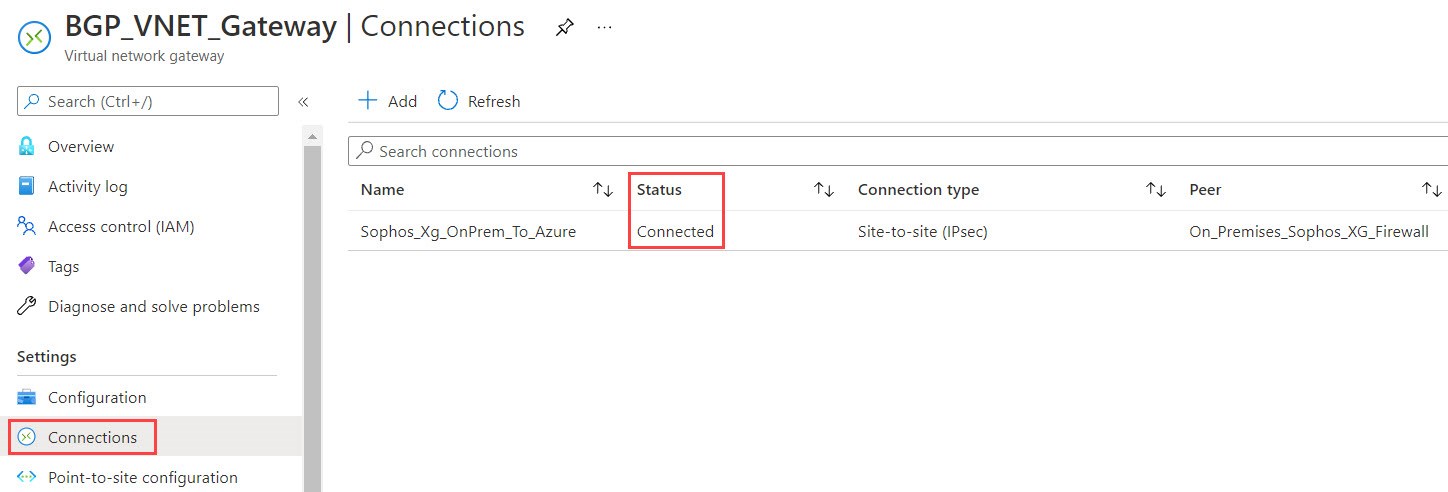
- Click the connection and ensure that you’re seeing data flow.
- If you see 0B, it does not mean that the connection isn’t working. It just means that there’s no data flow detected on the Azure side.
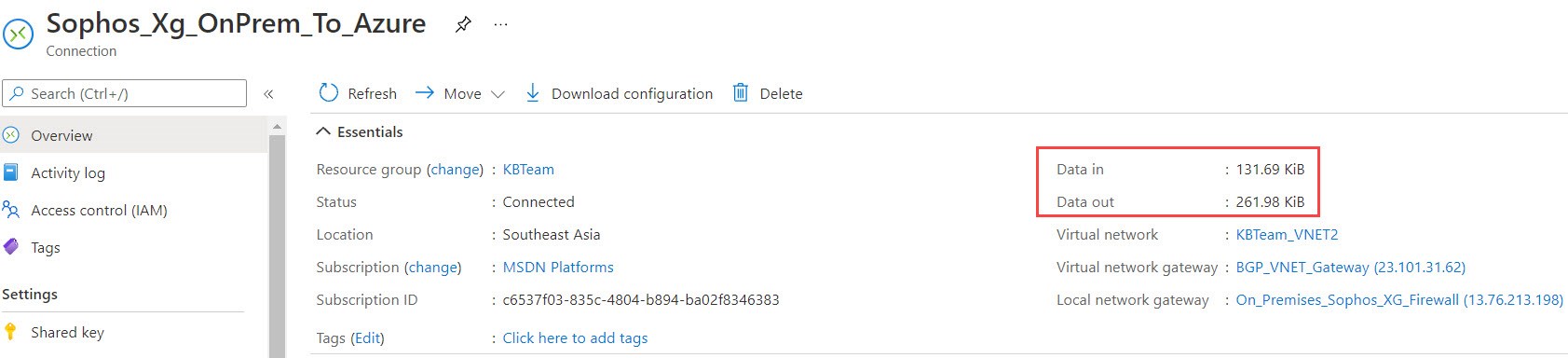
- If you see 0B, it does not mean that the connection isn’t working. It just means that there’s no data flow detected on the Azure side.
Things to watch out for
- Network Security Groups in Azure
- If there’s a network security group configured to block ports you’re attempting to connect on. This will cause issues.
- Route Table configuration in Azure
- By default, the VPN Gateway automatically advertises the VPN subnets to the vNet route tables, but watch out if you have user-defined routes that could override this.
Added link to KB 000043162 in step 1
[edited by: Dennis Huagan at 12:46 AM (GMT -8) on 1 Feb 2024]


