Special thanks to Mark Lanczak-Faulds and IsmailJaweedfor their contributions to this content!
Disclaimer: This information is provided as-is for the benefit of the Community. Please contact Sophos Professional Services if you require assistance with your specific environment.
Overview
This article provides an efficient way to find and delete inactive or unused devices rather than going through them manually in Sophos Central.
Why do you need to clear your old devices from Sophos Central?
When you uninstall the agent locally from an endpoint, the device listed in Sophos Central corresponding to the endpoint will remain.
Currently, the Sophos Central Active Directory (AD) Sync Utility supports synchronizing AD users and user groups, devices, and OUs, however, we don’t have a native method to remove old or inactive devices automatically.
What To Do?
There are two (2) options to do this, both require you to use the Sophos Central API.
- The first option is somewhat of a manual process. Use the Sophos Central API to gather information, then manually cross-reference those devices against your list of devices. You can then create a script that will delete devices using the Sophos Central API.
- The second option is an automated process using the Sophos Central API together with the Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) and Security Automation and Orchestration (SOAR) tool.
Demo scripts to gather and delete inactive devices will be provided at the end of this article.
To do the second option, some guideline questions you will need to start with are as follows:
- What data will you need to collect to help determine whether you can delete a device or not?
- What happens if an active device is deleted automatically?
- What tools do you have to assist with this process?
For a quick overview, below is a process diagram that covers the basic components of our process as a template for you to implement into your own environment and processes.
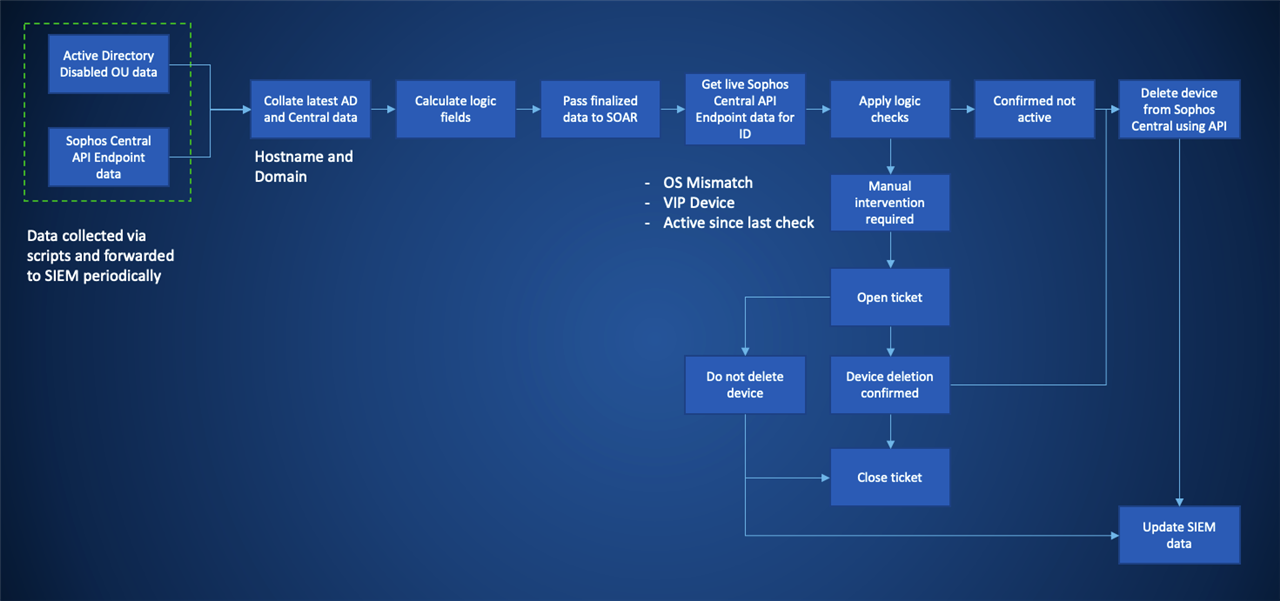
What data is needed?
Most organizations use Active Directory as the single source of truth for devices and users. You will need to monitor the latest changes in the Disabled OU or equivalent location dependent on how your organization manages retired devices and rebuild processes. Important fields from this data source are:
- Hostname
- Domain
- Distinguished Name
- Operating System
- Operating System Build Number
We also need to establish the current devices in Sophos Central. We can gather an inventory list of devices using the Sophos Central API. The fields will be gathered using the Sophos Central get endpoint API.
Key data fields for this process are:
- hostname
- id
- lastSeenAt
- os
o name
o build
- type
- associatedPerson
o name
o viaLogin
- tenant
o id
Together, these will form a solid base to help determine which systems are potential candidates for deletion.
How can we validate the AD and Central data?
The data is correlated using the hostname and domain of the device. In an ideal world, we would want to have a universally unique identifier (UUID) that ties them together. You may have another method that works in your environment to achieve this correlation.
Once the two data sources are correlated, we need to establish some comparatives before we pass the data to a SOAR tool for processing to ensure there is some logic to handle the events.
Important Steps:
Our aim for this process is to remove devices from Sophos Central which are no longer active. To achieve this without deleting valid devices, we also need to think of likely scenarios when we don’t want to delete a device.
● Determine device inactive period
The purpose of this is to allow a sensible period of inactivity for a system in the disabled OU. By only returning those devices inactive above a certain period of time, we are less likely to delete a device which may not need to be deleted from Sophos Central.
○ Convert lastSeenAt field to Unix epoch time using strptime, lastSeenAt format is: “2019-09-23T12:02:01.700Z”
○ Calculate how many days since device was last seen: (now() Unix epoch – lastSeenAt Unix epoch)/86400
● Validate whether the OS build matches
There could be a situation where the hostname and domain match a system in the inventory where the OS build does not match. In this instance, this device should have a flag set for manual intervention to avoid errors. The best method is comparing the OS build of the device against the data from Sophos Central.
● Automation
We now have several systems identified in the data which could be deleted from Sophos Central. Using a SOAR platform will allow you to pass each event through a flow process to determine what should happen to the device.
By checking the data you have from your SIEM against live Sophos Central Endpoint API data, you can make a final validation that the device is indeed inactive and can be deleted.
In addition to the automation aspect of deleting devices, we also need to do some auditing and perhaps include some scenarios to enforce manual intervention before deletion can be authorized.
Best Practices:
● Monitor VIP devices
To avoid unintentional deletion of devices for VIP users, we would advise flagging these devices for manual intervention to verify whether the device can be deleted from Sophos Central. One possibility is using a specific user AD group to define who these users are.
● Finding active devices
After comparing a device’s last activity with the data from the SIEM and that obtained through the live Sophos Central API query, it’s calculated that the device has reported back into Sophos Central recently. These machines should be raised for manual validation before they are deleted.
● Avoid duplication of processing
Logging which devices have been deleted allows for auditing and exclusion of these systems when collating the information at the start of the process.
● Track active processing which has been passed for manual intervention
Where devices require manual intervention and a Case is opened, it is recommended to log these and exclude them from future processing while the case is open. As part of the SOAR process intervention, this can be automated. Once the relevant response is received, the change can be made. Whether the device is deleted or not, it is noted, the Case is updated, and the Case log is removed as active.
● Track deletion failures
It is recommended to also flag failures to delete or verify device information so manual intervention can be applied to these.
Additional Steps:
In the event of incorrectly removing a device, the following steps are required to protect the endpoint:
- If the host does not have Sophos Endpoint Protection installed, simply download the latest installer from Sophos Central and install it to the endpoint.
- If the endpoint already has Sophos Endpoint Protection installed and Tamper Protection is not enabled, first uninstall Sophos Endpoint Protection, and install using the latest installer from the correct Sophos Central tenant.
- If Sophos Endpoint Protection is installed and Tamper Protection is enabled, please follow the steps below:
1. Log on to the correct Sophos Central tenant: https://cloud.sophos.com/manage/login
2. Go to Logs & Reports > Endpoint & Server Protection > Recover Tamper Protection passwords (Passwords will remain in this report for 90 days after deletion)
3. Search for the hostname and click ‘View details’ to view the latest Tamper Protection password that was active on the device prior to deletion.
4. Open Sophos Endpoint Protection UI on the device
5. Click on ‘Admin login’ and enter the Tamper Protection Password
6. Select ‘Settings’ and tick the box ‘Override Sophos Central Policy for up to 4 hours to troubleshoot.
7. Under ‘Control on Users’ turn off Tamper Protection
8. Uninstall Sophos Endpoint Protection
9. Reinstall Sophos Endpoint Protection with the latest installer from the correct Sophos Central tenant.
Final Steps:
With the basic building blocks in place, you are ready to dry-run the automation flow. Some key milestones are:
- In your chosen SOAR platform, be sure to disable the final action to delete the device before testing.
- Validate whether each device meets its expected outcome before committing to delete.
- When going live with the automation, start off by deleting devices slowly. This will allow time to further fine-tune your process.
- Reach out to your AD admins and service desk teams for feedback. They can provide valuable insights into the process and could highlight a key point that may have been overlooked.
Sample Python to gather devices
Gather old device data
To gather old devices to check against AD, please use the following code example (you will need to have the Sophos Central API Connector installed). This will create JSON files of the devices.
You will need to change ‘find_old’ and ‘client_id’ variables.
# Demo code sample using Sophos Central API connector. Not intended for production use.
import getpass
import logging
from sophos_central_api_connector import sophos_central_api_tenants as api_tenant
from sophos_central_api_connector import sophos_central_api_auth as api_auth
from sophos_central_api_connector import sophos_central_api_connector_utils as api_utils
from sophos_central_api_connector import sophos_central_api_get_data as get_api
from sophos_central_api_connector.sophos_central_api_output import process_output_json as json_output
from sophos_central_api_connector.config import sophos_central_api_config as api_conf
def main():
log_level = "INFO"
log_name = log_level
level = getattr(logging, log_name)
logging.basicConfig(level=level, format='%(asctime)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s',
datefmt='%d/%m/%Y %I:%M:%S %p')
logging.info("Start of Logging")
# Enter the variable to set how old devices you wish to return. E.g. for more than 30days enter '-P30D'
find_old = "<ADD IN TIME>"
# Enter your Sophos Central API Client ID (This is generated when setting up Sophos Central API credentials)
client_id = "<ADD IN YOUR CLIENT ID>"
# Set authorisation and whoami URLs
auth_url = api_conf.auth_uri
whoami_url = api_conf.whoami_uri
partner_url = api_conf.tenants_ptr_uri
organization_url = api_conf.tenants_org_uri
# Get client secret by prompting user
client_secret = getpass.getpass(prompt="Provide Sophos Central Secret ID: ", stream=None)
# Get Sophos Central API Bearer Token for authorisation
sophos_access_token = api_auth.get_bearer_tok(client_id, client_secret, auth_url)
# Construct id_headers
headers = api_auth.validate_id_headers(sophos_access_token)
# Lookup up the unique ID assigned to the business entity for Sophos Central API
whoami_id, whoami_type, whoami_data = api_auth.get_whoami_data(headers, whoami_url)
# Obtain correct whoami uri/header based on the whoami type
header_type, tenant_url = api_auth.validate_whoami_type(whoami_type, whoami_data, partner_url, organization_url)
# Construct tenant headers
tenant_headers = api_tenant.gen_tenant_headers(headers, whoami_id, whoami_type, header_type)
# Check and gather tenant information
if whoami_type == "tenant":
tenant_info = api_tenant.type_tenant(tenant_headers, whoami_id, tenant_url, sophos_access_token)
else:
tenant_info = api_tenant.get_tenant_info(headers, tenant_url, sophos_access_token)
# Generate urls for tenants
api = "endpoint"
page_size = "50&lastSeenBefore={0}&fields=tenant&fields=hostname&fields=id&fields=lastSeenAt&fields=os&fields=type&fields=associatedPerson".format(find_old)
# Generate tenant url data
tenant_url_data = api_utils.generate_tenant_urls(tenant_info, page_size, api, from_str=None, to_str=None)
for ten_id, ten_item in tenant_url_data.items():
# Pass the ten_url_data and gather devices
tenant_id = ten_id
# get data information for the tenant in the loop
json_data = get_api.get_data(tenant_url_data, page_size, tenant_id, api)
filename = tenant_url_data[tenant_id]['filename']
json_output(json_data, filename, api)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
Delete identified devices in Sophos Central
To delete the identified assets you can edit the JSON that was gathered previously and remove any devices which should not be deleted. The demo script assumes the JSON file is in the same location as the script. You will need to change ‘client_id’ variable.
# Demo code sample using Sophos Central API connector. Not intended for production use.
import getpass
import logging
import os
import json
import requests
from sophos_central_api_connector import sophos_central_api_tenants as api_tenant
from sophos_central_api_connector import sophos_central_api_auth as api_auth
from sophos_central_api_connector import sophos_central_api_connector_utils as api_utils
from sophos_central_api_connector.config import sophos_central_api_config as api_conf
def main():
log_level = "INFO"
log_name = log_level
level = getattr(logging, log_name)
logging.basicConfig(level=level, format='%(asctime)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s',
datefmt='%d/%m/%Y %I:%M:%S %p')
logging.info("Start of Logging")
# Enter your Sophos Central API Client ID (This is generated when setting up Sophos Central API credentials)
client_id = "<ADD IN YOUR CLIENT ID>"
# Set authorisation and whoami URLs
auth_url = api_conf.auth_uri
whoami_url = api_conf.whoami_uri
partner_url = api_conf.tenants_ptr_uri
organization_url = api_conf.tenants_org_uri
# Get client secret by prompting user
client_secret = getpass.getpass(prompt="Provide Sophos Central Secret ID: ", stream=None)
# Get Sophos Central API Bearer Token for authorisation
sophos_access_token = api_auth.get_bearer_tok(client_id, client_secret, auth_url)
# Construct id_headers
headers = api_auth.validate_id_headers(sophos_access_token)
# Lookup up the unique ID assigned to the business entity for Sophos Central API
whoami_id, whoami_type, whoami_data = api_auth.get_whoami_data(headers, whoami_url)
# Obtain correct whoami uri/header based on the whoami type
header_type, tenant_url = api_auth.validate_whoami_type(whoami_type, whoami_data, partner_url, organization_url)
# Construct tenant headers
tenant_headers = api_tenant.gen_tenant_headers(headers, whoami_id, whoami_type, header_type)
# Check and gather tenant information
if whoami_type == "tenant":
tenant_info = api_tenant.type_tenant(tenant_headers, whoami_id, tenant_url, sophos_access_token)
else:
tenant_info = api_tenant.get_tenant_info(headers, tenant_url, sophos_access_token)
# Generate urls for tenants
api = "endpoint"
page_size = None
# Generate tenant url data
tenant_url_data = api_utils.generate_tenant_urls(tenant_info, page_size, api, from_str=None, to_str=None)
logging.info("Creating device deletion URLs...")
for file in [os.path.basename(file) for file in os.listdir() if file.endswith(".json")]:
with open(file, 'r', encoding='utf8') as device_file:
logging.info("Processing file: {0}".format(file))
device_dict = json.load(device_file)
for ten_id, ten_item in tenant_url_data.items():
tenant_id = ten_id
for item in device_dict.values():
tenant_ref = item['tenant']['id']
if tenant_ref == tenant_id:
orig_url = ten_item['orig_url']
headers = ten_item['headers']
device_id = item["id"]
endpoint_url = "{0}/{1}".format(orig_url, device_id)
del_ep = requests.delete(endpoint_url, headers=headers)
del_sc = del_ep.status_code
logging.info("Device ID: {0}, deletion status: {1}".format(device_id, del_sc))
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
Additional References:
Get all the endpoint installer links for a tenant
Get Tamper Protection settings for a specified endpoint
Edit Ticket to Case
[edited by: GlennSen at 4:28 AM (GMT -8) on 24 Jan 2024]
