This guide covers best-practices for hardening your Sophos Firewall but should also be applied to all your network infrastructure from Sophos or any other vendor. Download a PDF version.
Table of Contents
- Keep Your Firmware Updated
- Limit Device Service Access
- Use Strong Passwords, Multi-Factor Authentication, and Role-Based Access
- Minimize Access to Internal Systems
- Enable Appropriate Protection
- Enable Alerts and Notifications
Keep Your Firmware Updated
Every Sophos Firewall OS update includes important security enhancements. Ensure you keep your firmware up to date under Backup & Firmware > Firmware. Check at least once a month for firmware updates in Sophos Central or the on-box console. Deploy every update including all maintenance releases (MRs) as every update may include important security fixes.
You can easily schedule updates in Sophos Central to be applied during a period of minimal disruption.
If you don’t have one already, consider a High-Availability (HA) deployment which has the benefit of being able to upgrade device firmware without disruption.
Keep up to date on the latest firmware updates and news on the Sophos Firewall Community
Helpful Links:
Limit Device Service Access
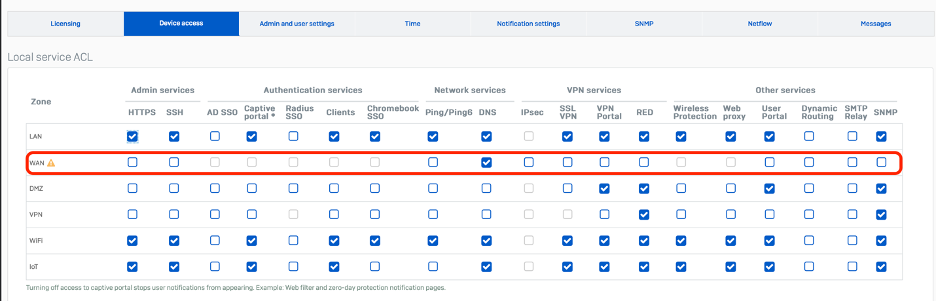
It’s critically important that you disable non-essential services on the WAN interface which exposes them to the Internet. In particular, HTTPS and SSH admin services. To manage your Firewall remotely, Sophos Central offers a much more secure solution than enabling WAN admin access. Alternatively, use ZTNA for remote management of your network devices.
Check your local services access control under Administration > Device Access and ensure no items are checked for the WAN Zone unless absolutely necessary.
Also be sure to lock down admin access from your internal LAN as well by ensuring admin interfaces are either disabled or only accessible from specific trusted LAN IPs.
For remote users, consider ZTNA which is much more secure than VPN, however if using VPN, utilize the new hardened containerized VPN Portal and only enable it when configurations change and users need to update – otherwise keep it disabled. Disable User Portal access on the WAN and provide access via VPN only. Use multi-factor authentication on all portals (see below).
Helpful Links:
Use Strong Passwords, Multi-Factor Authentication, and Role-Based Access
Enable Multi-Factor Authentication or One Time Password (OTP) and enforce strong passwords across all admin and user accounts which will protect your Firewall from unauthorized access either from stolen credentials or brute force hacking attempts. Ensure your sign-in security settings are set to block repeated unsuccessful attempts and enforce strong passwords and CAPTCHA. Also use role-based access controls to limit exposure.
Helpful Links:
- Multi-factor Authentication (MFA).
- Admin and Sign-in Security Settings
- Device Role-Based Access
- VPN and User Portals
Minimize Access to Internal Systems
Any device exposed to the WAN via a NAT rule is a potential risk. Ideally, no device should be exposed to the internet via NAT or inbound connections, including IoT devices.
Audit and review all your NAT and Firewall Rules regularly to ensure there are no WAN to LAN or remote access enabled. Conduct regular tests and audits of firewall rules to spot risky configuration drift, paying particularly focus on services exposed to the WAN side of the device.
Use ZTNA (or even VPN) for remote administration and access to internal systems – DO NOT expose these systems, especially Remote Desktop access to the Internet. For IoT devices, shut down any devices that do not offer a cloud proxy service and require direct access via NAT - these devices are ideal targets for attackers.
Helpful Links:
Enable Appropriate Protection
Protect your network from exploits by applying IPS inspection to incoming untrusted traffic via relevant firewall rules. Ensure you don’t have any broad firewall rules that allow ANY to ANY connections.
Also protect your network from both DoS and DDoS attacks by setting and enabling protection under Intrusion Prevention > DoS & spoof protection. Enable spoof prevention and apply flags for all DoS attack types.
Block traffic from regions you don’t do business with by setting up a firewall rule to block traffic originating from unwanted countries or regions.
Ensure Sophos X-Ops threat feeds are enabled to log and drop under Active Threat Protection.
Use Network Detection and Response (NDR) to monitor traffic to/from the firewall as well as traffic flowing through the firewall for possible attacks.
Helpful Links:
Enable Alerts and Notifications
Sophos Firewall can be configured to alert administrators of system-generated events. Administrators should review the list of events and check that system and security events are monitored to ensure that issues and events can be acted upon promptly. Notifications are sent via either an email and/or to SNMPv3 traps. To configure Notifications, navigate to Configure > System services and select the Notifications list tab.
Also ensure your firewalls are sending logs to Sophos Central and/or your SIEM of choice.
Helpful Links:
