Disclaimer: This information is provided as-is for the benefit of the Community. Please contact Sophos Professional Services if you require assistance with your specific environment.
Table of Contents
Overview
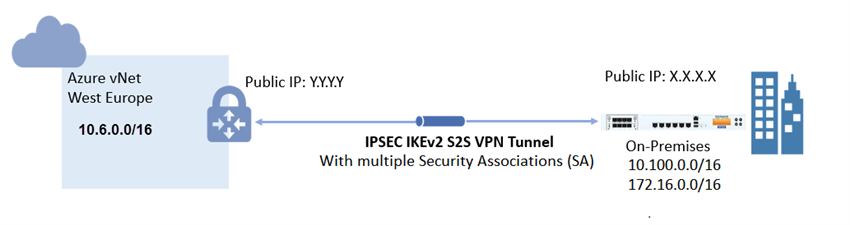
Microsoft Azure supports two types of VPN Gateway: Route-based and policy-based. To use IKEv2, you must select the route-based Azure VPN Gateway.
This article describes the steps to configure a site-to-site IPsec VPN with multiple SAs to a route-based Azure VPN gateway.
Product and Environment
Sophos Firewall
Configure Azure
Create a local network gateway
The local network gateway typically refers to the on-premises location. You'll need the public IP address of the on-premise Sophos Firewall and its private IP address spaces.
- Login to Microsoft Azure. In the search box, type local network gateways and select Local network gateways.
- In the Local network gateways blade, click + Add and configure the following in the Create local network gateway blade:
- Name: On_Prem_Sophos_XG_Firewall (You can choose any preferred name).
- Endpoint: IP address
- IP address: Specify the Sophos Firewall's public IP address.
- Address space: Specify the on-premises address ranges. If multiple address space ranges are needed, make sure that the specified ranges here do not overlap with ranges of other networks that you want to connect to. Azure will route the specified address range to the on-premises VPN device IP address.
- Subscription: Select or verify the correct subscription.
- Resource group: Select the resource group, you can either create a new resource group or select an existing one.
- Location: Select the location in which this object will be created. You may want to select the same location that your VNet resides in, but you are not required to do so.
Create a gateway subnet
The VPN gateway is deployed into a specific subnet of your network called the Gateway subnet. The size of the Gateway subnet that you specify depends on the VPN gateway configuration that you want to create. While it is possible to create a Gateway subnet as small as /29, it is recommended to create a larger subnet that includes more addresses by selecting /27 or /28 to be able to accommodate future configurations.
- In the search box, type Virtual networks and select Virtual networks.
- Click the virtual network for which you want to create a virtual network gateway, in this example, sophos_azure_vnet is used.
- In the Virtual network blade, under Settings, click on Subnets.
- In the Subnets blade, click on + Gateway subnet.
- In the Add subnet blade, configure the CIDR range of the new gateway subnet.
Create the VPN gateway
- In the search box, type Virtual network gateways and select Virtual network gateways.
- In the Virtual network gateways blade, click on + Add and configure the following in the Create virtual network gateway blade:
- Subscription: Verify that the correct subscription is selected for the deployment.
- Name: Name your gateway. This is not the same as naming a gateway subnet. It's the name of the gateway object you are creating.
- Region: Select the same location as your virtual network (otherwise the virtual network will not be displayed on the list).
- Gateway type: VPN
- VPN type: Route-based (this is a MUST to be able to use IKEv2).
- SKU: Select the gateway SKU from the drop-down list. For more information about gateway SKUs, see Gateway SKUs.
- Generation: Generation 1
- Virtual network: Choose the virtual network to which you want to add this gateway.
- Select the vNet that you created in the Gateway subnet earlier. In this example, the vNet is sophos_azure_vnet created earlier.
- If the virtual network that you want is not displayed on the list, verify that you have selected the right location in the "Region" parameter above.
- Public IP address: You need a public IP address. Do the following to obtain one.
- Select Create new to create a new public IP resource (you can select Use existing to use an existing public IP resource)
- Input a Name for your public IP address
- The public IP address SKU is usually automatically selected based on your VPN Gateway SKU.
- Leave other settings as default.
- Click Review + create.
- Click on Create.
-
Note: Creating a gateway can take up to 45 minutes.
- After the VPN gateway creation has successfully completed, click the Refresh button on the Virtual network gateways blade to display the newly deployed VPN gateway.
-
Click on the VPN gateway created earlier, in this example, TE_Sophos_Azure_VPN_Gateway. In the Virtual network Gateway blade, select Overview and make a note of the newly assigned public IP address of this gateway.
Create the VPN connection
- In the Azure Portal: https://portal.azure.com, in the top right corner, click on the Cloud Shell icon.
- A new pane will open below your existing window, select PowerShell.
- If this is your first time using the Cloud Shell, you will be prompted to create a storage account, select your Subscription and click on Create storage.
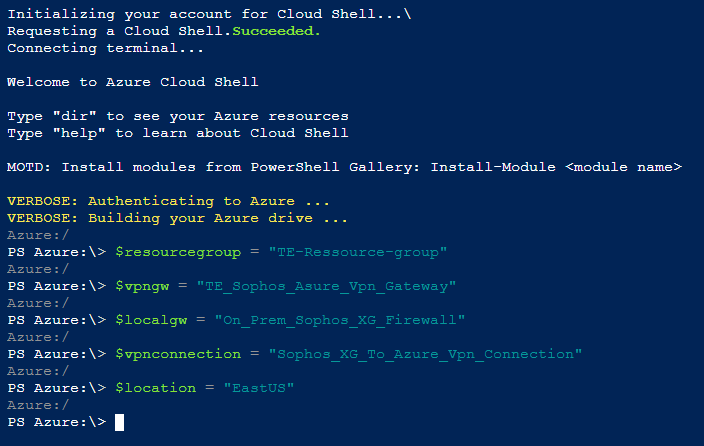
- Set the following variables replacing the values with your environment's values.
$resourcegroup = "name_of_the resource_group_for_the_connection"
$vpngw = "name_of_the_azure_vpn_gateway_created_earlier"
$localgw = "name_of_azure_local_gateway_created_earlier"
$vpnconnection = "name_for_the_vpn_connection"
$location = "location_of_the_vpn_connection" - Create the IPsec policy that will be used for the connection.
$ipsecpolicy = New-AzureRmIpsecPolicy -IkeEncryption AES256 -IkeIntegrity SHA256 -DhGroup DHGroup2 -IpsecEncryption AES256 -IpsecIntegrity SHA256 -PfsGroup None -SALifeTimeSeconds 27000
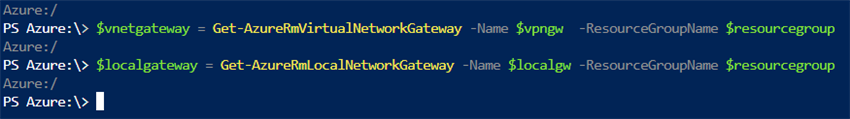
- Get the virtual network gateway and local network gateway resources and store them in a variable
$vnetgateway = Get-AzureRmVirtualNetworkGateway -Name $vpngw -ResourceGroupName $resourcegroup
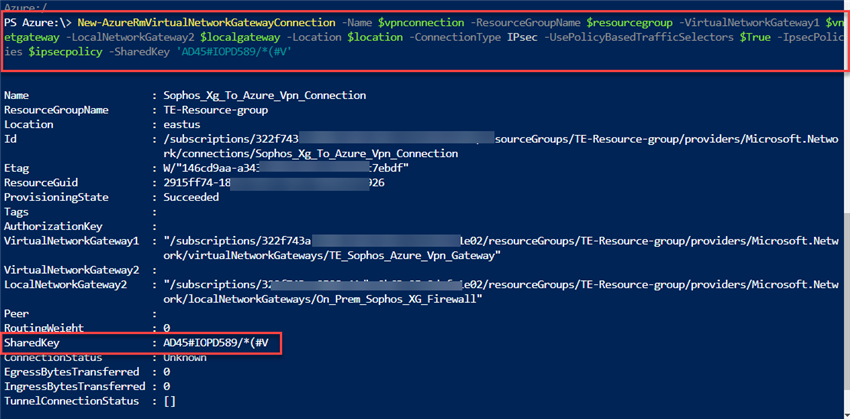
$localgateway = Get-AzureRmLocalNetworkGateway -Name $localgw -ResourceGroupName $resourcegroup - Create the VPN connection and set the UsePolicyBasedTrafficSelectors parameter to true (Replace "shared_secret_key" with your shared secret key value)
New-AzureRmVirtualNetworkGatewayConnection -Name $vpnconnection -ResourceGroupName $resourcegroup -VirtualNetworkGateway1 $vnetgateway -LocalNetworkGateway2 $localgateway -Location $location -ConnectionType IPsec -UsePolicyBasedTrafficSelectors $True -IpsecPolicies $ipsecpolicy -SharedKey 'shared_secret_key'
Configure Sophos Firewall
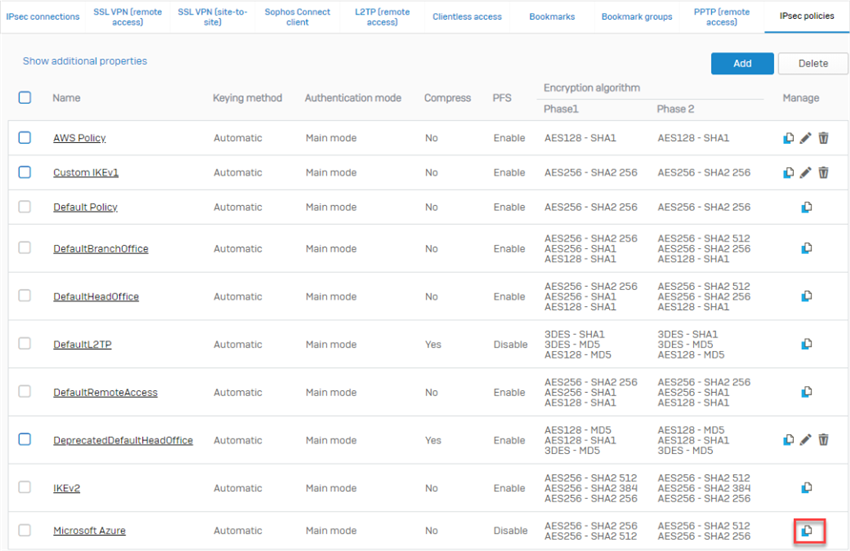
- Go to VPN > IPsec policies to clone the default Microsoft Azure policy.
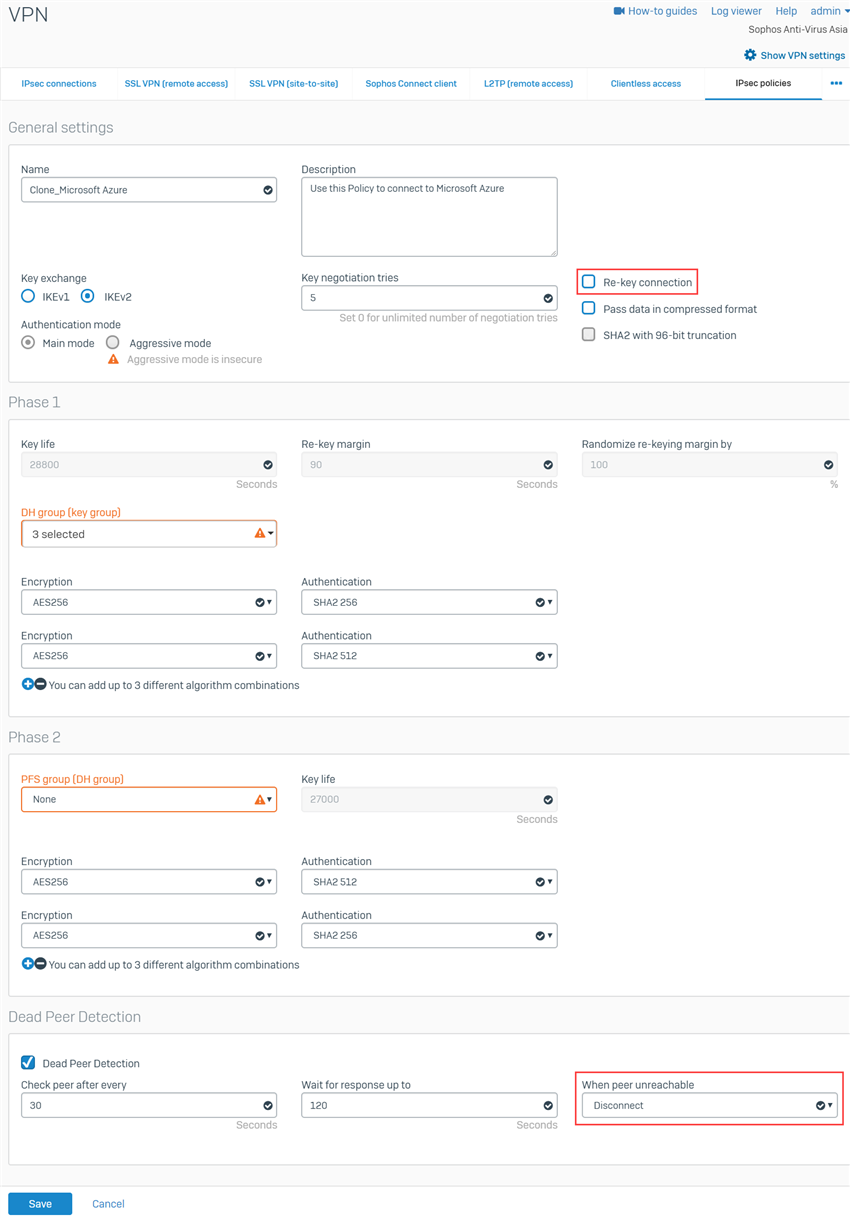
- In the cloned Microsoft Azure policy, disable Re-key connection. Under Dead Peer Detection section, set When peer unreachable to Disconnect. Keep the rest as is. We do this because Azure does not support re-keying from the remote peer and the Gateway type will be set to Respond only. Click Save.
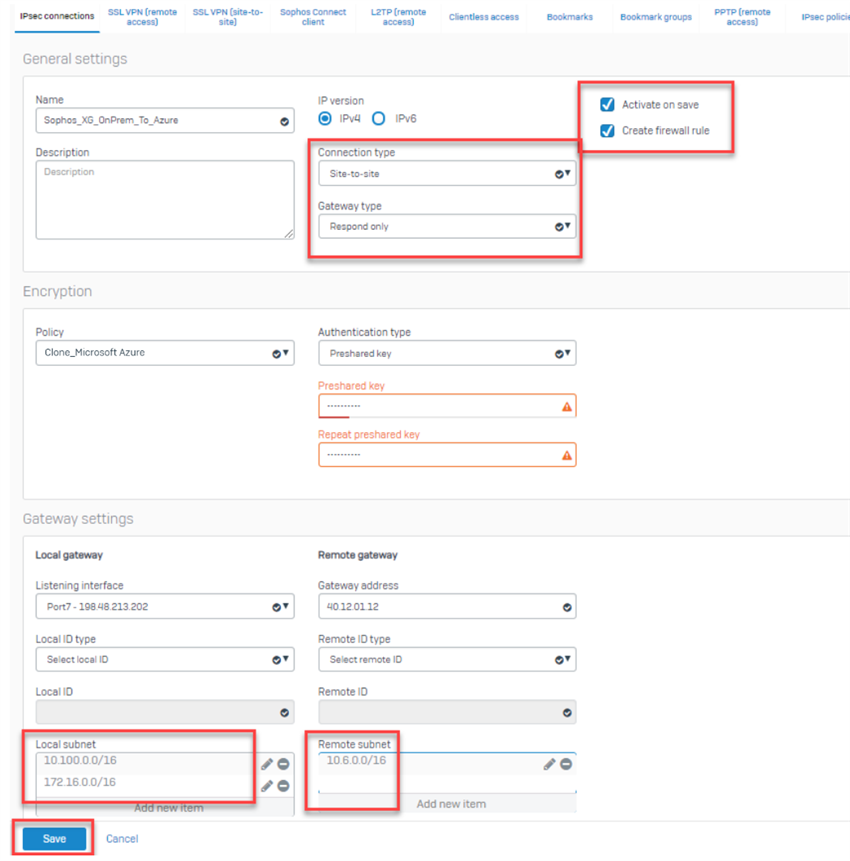
- Go to VPN > IPsec Connections, select Add and configure the following settings:
- General Settings:
- Name: Input any preferred name.
- IP Version: IPv4.
- Activate on Save: Selected.
- Create firewall rule: Selected.
- Description: Add a description for the connection.
- Connection Type: Site-to-Site.
- Gateway Type: Respond only.
- Encryption:
- Policy: The recently cloned Microsoft Azure.
- Authentication Type: Preshared Key.
- Preshared Key: Enter the same preshared key that you entered when creating the VPN connection on Azure.
- Repeat Preshared Key: Confirm the above preshared key.
- Gateway Settings:
- Listening Interface: Select the WAN interface of the Sophos Firewall.
- Gateway Address: Input the public IP of the Azure VPN gateway noted earlier.
- Local Subnet: Select the CIDR ranges of your local networks. This subnet is behind the on-premises Sophos Firewall.
- Remote Subnet: Select the CIDR ranges of your Azure network. This subnet is behind the Azure virtual network gateway.
- Advanced: leave the default settings.
- General Settings:
- Upon clicking Save, the IPsec connection is activated and the tunnel should be established successfully.
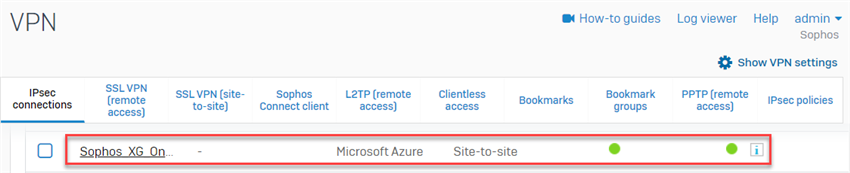
Note:
- Make sure that the connection is active. If not, click on the button under the Active column.
- Do not click on the button under the Connection column as it will override the configuration settings set on the IPsec connection (Gateway type: Respond only). This is to avoid issues since Azure must initiate the tunnel.
- Go to Network > Interfaces to edit the public-facing interface. Under Advanced settings, enable Override MSS and set its value to 1350.
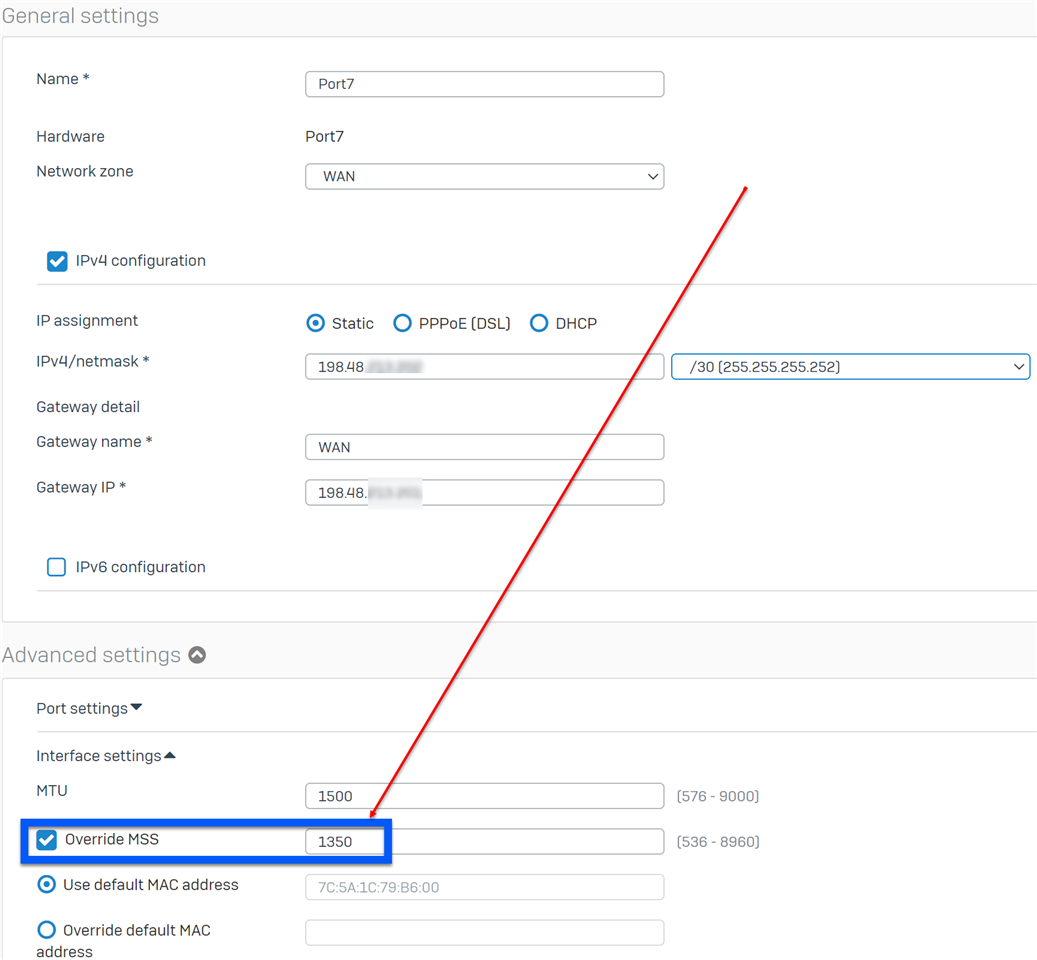
This is because any packets larger than an MSS of 1350 bytes hitting the Azure virtual network through its gateway will get segments and some fragments may get dropped in the Azure platform across the VPN datapath. For more information, please refer to About VPN devices and IPsec/IKE parameters for Site-to-Site VPN Gateway connections.
Results
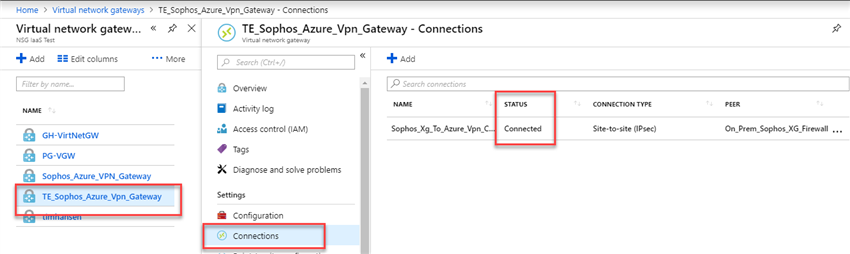
- In the Azure Portal: https://portal.azure.com, in the search box, type Virtual network gateways and select Virtual network gateways.
- Select the VPN gateway created earlier, in the Virtual network gateway blade select Connections and verify that its status is connected.
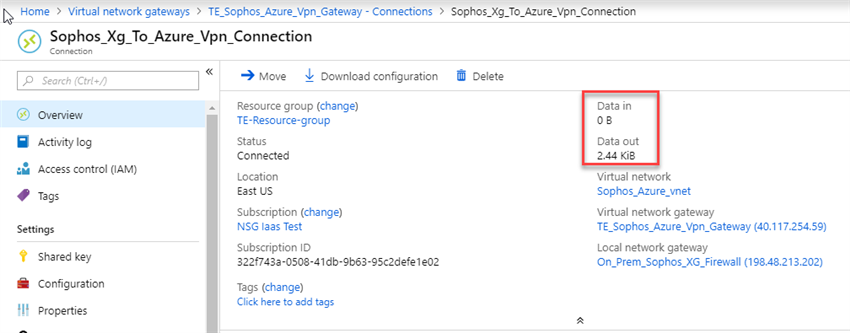
- Click on the connection to verify ingress and egress traffic flow.
- From Sophos Firewall, go to Current activities > IPsec connections and verify both connections to both subnets.
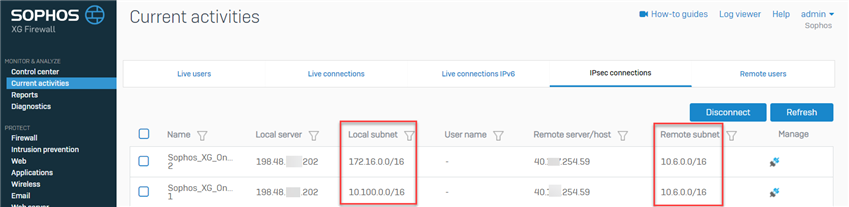
Note:
- An interface with a public routable IP is required on the on-premises Sophos Firewall as Azure do not support NAT. For further information, please refer to Azure VPN Gateway FAQ.
- If the on-premises Sophos Firewall appliance is behind a NAT device, The recommendation is to use a Sophos Firewall in Azure to deploy the VPN connection. Please refer to Sophos Firewall: Quick Start Guide on Microsoft Azure to deploy the Sophos Firewall on Azure.
- Azure must re-key the IKE_SA by deleting the expired IKE_SA and creates a new connection, which leads to some seconds of downtime.
- Azure tends to use SHA1 if not forced by the on-premises Sophos Firewall to use SHA2.
Added TAG
[edited by: Erick Jan at 5:57 AM (GMT -7) on 28 Oct 2024]